Introduction to Marketing Channels
In the simplest terms, marketing channels refer to the various methods and pathways through which products or services move from the producer to the final consumer. These channels form an essential part of business strategy as they determine how products will reach their intended audiences. By understanding marketing channels, companies can choose the most effective way to distribute their products, ensuring they reach the right customer at the right time and place. These channels are critical because they help businesses maximize their sales, build brand awareness, and maintain customer loyalty.
When a company designs its marketing strategy, the selection of the right channels is crucial. Without an effective channel structure, even the best product might fail to reach its potential. This is why businesses invest heavily in understanding the dynamics of marketing channels—because they form the bridge between production and consumption.
The Basics of Marketing Channels
A marketing channel essentially acts as the route or mechanism that carries a product or service from the point of production to the end user. These channels typically involve various intermediaries who help facilitate the movement of goods. At the heart of marketing channels is the concept of distribution: getting products into the hands of consumers efficiently and effectively. Without a well-organized channel, companies may struggle to meet demand, which can lead to lost sales or diminished customer satisfaction.
Marketing channels can vary depending on the type of product, target market, and business objectives. For instance, a company selling luxury goods may opt for direct selling to maintain control over the brand experience, while a consumer electronics company might work with a network of retailers and wholesalers to distribute its products widely. Thus, understanding how marketing channels work is essential for crafting strategies that align with a business’s goals.
Types of Marketing Channels
There are several types of marketing channels, and each one has its distinct characteristics. The most common types include:
- Direct Marketing Channels – This is when a producer sells directly to the consumer without any intermediaries. Direct selling is often used for high-value products or services that require personal attention or customization, such as real estate or high-end consulting services.
- Indirect Marketing Channels – These channels involve intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, or agents who facilitate the sale of products. This method allows businesses to reach a larger audience quickly and efficiently. It’s commonly used by consumer goods manufacturers who want to distribute products on a mass scale.
- Hybrid Marketing Channels – A mix of both direct and indirect channels, where businesses may sell directly to some consumers while also leveraging intermediaries for broader reach. This approach can maximize exposure and create multiple touchpoints for potential customers.
Each of these channels comes with its advantages and disadvantages. Direct channels give businesses more control over customer interaction, while indirect channels can help them reach a broader audience. Hybrid channels, however, allow businesses to enjoy the benefits of both methods.
Components of a Marketing Channel
A marketing channel isn’t just about moving products from point A to point B; it involves multiple components working together to create value. One key component is the intermediary. These intermediaries act as the middlemen between the producer and the consumer, providing necessary services like warehousing, transportation, and promotion. Retailers, wholesalers, and agents are all examples of intermediaries that make the distribution of goods smoother and faster.
Another important element is the distribution process. This process involves a series of steps that ensure products reach the right place at the right time. Distribution involves decisions on how goods are stored, shipped, and managed. Distribution centers, warehouses, and logistics services are essential in facilitating this process.
Lastly, marketing channels help in creating value for the customer by ensuring they can access products that meet their needs at a reasonable cost. The convenience of purchasing a product through an online store, for example, is a form of value creation that wouldn’t exist without an efficient marketing channel.
Direct vs Indirect Marketing Channels
Direct marketing channels are those where the producer communicates directly with the consumer, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This model is often seen in business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions, especially for high-end or specialized products. Direct channels enable businesses to have full control over their brand, messaging, and customer experience. For example, companies like Apple and Tesla often sell directly through their own stores or websites.
On the other hand, indirect marketing channels involve the use of intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, and agents, to distribute products to the consumer. This method allows businesses to reach a larger audience by leveraging the networks and infrastructure of third parties. Companies like Procter & Gamble use indirect marketing channels extensively, with their products being sold through a wide network of retailers, from supermarkets to online stores.
Each model has its own benefits. Direct channels allow for better customer relationships and more control over the product experience, but indirect channels often provide a wider reach and lower distribution costs.
The Role of Retailers and Wholesalers in Marketing Channels
Retailers and wholesalers are crucial components in marketing channels. Retailers are businesses or individuals who sell products directly to consumers. They provide consumers with easy access to goods in convenient locations, whether physical stores or online platforms. Retailers also play a key role in promoting products and influencing consumer purchase decisions through various marketing tactics like advertising, promotions, and customer service.
Wholesalers, on the other hand, act as intermediaries who buy products in bulk from manufacturers and then sell them to retailers or other businesses. Wholesalers help reduce the complexity of reaching multiple retailers or customers and often deal with large quantities of products. They are particularly important for businesses that need to scale quickly or distribute products to a wide geographic area.
Both retailers and wholesalers contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing channels by ensuring that products are available where and when consumers want them.
The Evolution of Marketing Channels in the Digital Age
In today’s world, marketing channels have evolved significantly, driven by technological advancements and changes in consumer behavior. The rise of e-commerce and digital marketing channels has transformed how businesses connect with their customers. Traditional brick-and-mortar stores, for example, no longer dominate the landscape as more consumers turn to online shopping. E-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify have become integral parts of modern marketing channels, providing businesses with direct access to a global audience.
Social media also plays a pivotal role in shaping marketing channels. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok enable businesses to engage directly with their target audiences, promote products, and drive traffic to their online stores. The integration of social commerce, where consumers can purchase directly from social media platforms, has blurred the lines between marketing and sales, making it easier for businesses to reach potential customers in real-time.
Moreover, the ability to track consumer behaviors through data analytics has allowed businesses to fine-tune their marketing strategies. Digital marketing channels, with their ability to gather insights into consumer preferences and behaviors, offer a more personalized approach to marketing. This data-driven strategy is helping companies enhance customer experiences, create targeted advertising campaigns, and improve sales conversions.
Marketing Channel Strategy
Creating a marketing channel strategy is crucial for businesses to navigate the complexities of distribution and reach their target customers effectively. A well-constructed strategy helps businesses optimize their channels, ensuring that they select the right mix of direct and indirect channels that align with their brand goals and customer needs.
One of the first steps in developing a marketing channel strategy is understanding the target market. Factors such as customer demographics, purchasing behavior, and geographical location play a key role in selecting the right channels. For example, younger audiences may prefer digital channels, while older generations might prefer physical retail stores. Companies must adapt their strategies to meet the evolving preferences of their customers.
Another consideration is the competition. Analyzing the channels used by competitors can provide insights into industry trends and help businesses identify gaps in the market. Additionally, companies must evaluate their resources and capabilities. For instance, a startup might not have the infrastructure to distribute products through a wide network of wholesalers, but they may excel in direct-to-consumer online sales.
Finally, businesses must ensure that their marketing channels are aligned with their overall business objectives. A clear understanding of the brand’s mission, vision, and goals will guide the channel strategy, ensuring that the business communicates a consistent message and provides a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints.
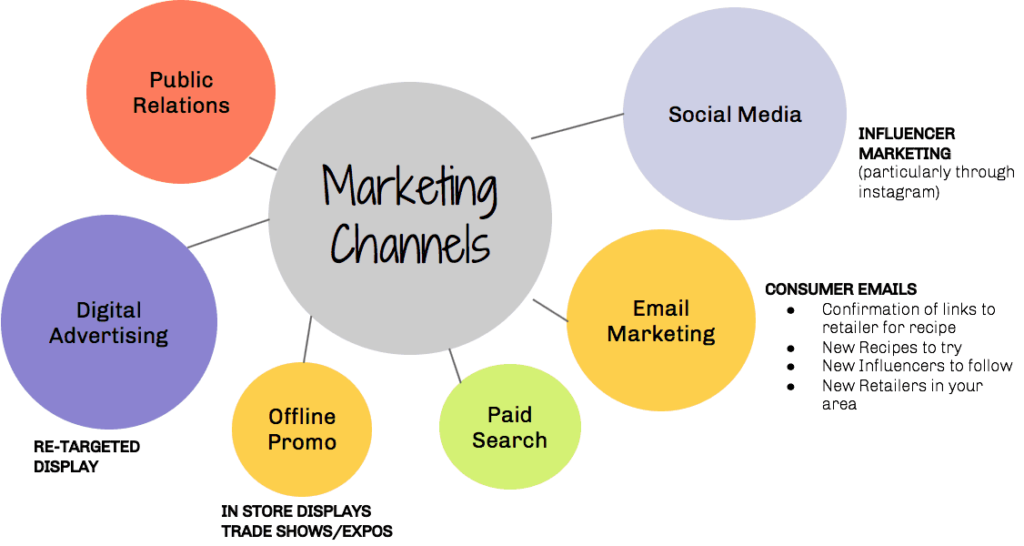
Selecting the Right Marketing Channel for Your Business
Choosing the right marketing channel can be challenging, especially when there are so many options available. Businesses need to consider several factors before deciding on the best channel or combination of channels. These factors include the type of product, customer behavior, budget, and market competition.
For example, businesses offering high-end products or services may benefit from direct marketing channels, where they can control the brand experience and offer personalized customer service. On the other hand, mass-market consumer goods often require indirect marketing channels to ensure wide distribution and affordability.
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting marketing channels is the customer’s buying behavior. Are they likely to shop online or visit a physical store? Do they prefer shopping through a mobile app or via social media? Understanding these preferences can help businesses tailor their marketing strategies to the appropriate channels.
Additionally, businesses need to evaluate their budget and resources. Direct marketing channels often require significant investment in technology, logistics, and customer service. Indirect channels, such as working with wholesalers and retailers, may require less upfront investment but may involve lower profit margins due to intermediary costs.
The Challenges of Marketing Channels
While marketing channels are essential for business success, they come with their own set of challenges. One of the primary challenges is channel conflict. This occurs when different parties within a marketing channel (such as manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers) have conflicting interests or goals. For example, a manufacturer may want to maintain control over pricing, while a retailer may want to offer discounts to attract customers.
Logistics and distribution are other major challenges. Efficiently managing the flow of goods from the producer to the consumer can be complicated, especially when dealing with multiple intermediaries across different geographical locations. Ensuring that products are delivered on time and in good condition requires a streamlined distribution network, which can be costly and time-consuming to maintain.
Another challenge is maintaining consistency across multiple channels. With the rise of omnichannel strategies, businesses must ensure that the customer experience is consistent, whether customers are shopping online, in-store, or through mobile apps. This can be difficult to achieve, especially when different channels operate under different management structures.
Finally, businesses need to stay ahead of the competition. As new marketing channels emerge, companies must adapt quickly to changing trends and customer behaviors. This means continually evaluating and adjusting marketing channel strategies to remain relevant and competitive.
The Role of Channel Management in Marketing Channels
Channel management refers to the process of overseeing and optimizing the performance of marketing channels. Effective channel management is essential for businesses to ensure that their marketing efforts are reaching the right customers through the right channels. Successful channel management involves fostering strong relationships with intermediaries, providing them with the necessary support, and resolving any conflicts that may arise.
Effective communication is a key component of channel management. Regular communication between manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and other intermediaries ensures that all parties are aligned and working toward the same goals. This collaboration helps to avoid misunderstandings and inefficiencies that could impact product availability, pricing, and customer satisfaction.
Channel management also involves monitoring performance to ensure that each channel is contributing to the overall success of the business. Businesses must track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales volume, customer satisfaction, and channel costs to assess the effectiveness of their marketing channels. This data helps identify areas for improvement and enables businesses to make data-driven decisions about channel optimization.
The Future of Marketing Channels
As technology continues to evolve, the future of marketing channels looks promising. One of the most significant trends is the rise of omnichannel strategies, where businesses integrate multiple channels to provide a seamless customer experience. Omnichannel strategies allow customers to interact with businesses across various touchpoints, whether online, in-store, or through mobile apps, while receiving consistent messaging and service.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is also transforming marketing channels. These technologies enable businesses to analyze customer data in real time, making it easier to predict customer needs and personalize marketing efforts. AI can also automate many aspects of marketing, such as customer service and content creation, further enhancing the efficiency of marketing channels.
Marketing Channel Examples in Different Industries
Different industries utilize marketing channels in unique ways, depending on their products and target markets. For example, the retail industry relies heavily on both physical and digital channels to reach customers. Retailers often combine traditional in-store experiences with e-commerce platforms to provide customers with a wide range of options for shopping.
In the tech industry, marketing channels are often used to distribute high-tech gadgets and software products. Companies like Apple and Microsoft utilize both direct and indirect channels, working with both physical retailers and online platforms to reach a global audience.
The service industry, on the other hand, may focus more on direct marketing channels, as services are often customized and require more personal interaction. Service providers such as consultants, financial advisors, and healthcare providers often rely on direct marketing methods such as referrals, word-of-mouth, and digital platforms to reach their clients.
Conclusion: The Importance of Marketing Channels in Business Success
In conclusion, marketing channels are integral to the success of any business, as they directly impact the ability to reach customers and deliver value. Whether a business chooses direct, indirect, or hybrid marketing channels, the key to success lies in selecting the right strategy that aligns with customer needs, business objectives, and available resources.
As marketing channels continue to evolve in the digital age, businesses must remain agile and responsive to changing trends and customer behaviors. By embracing new technologies, leveraging data-driven insights, and integrating multiple marketing channels, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and provide a superior customer experience.
FAQs about Marketing Channels
- What are the main types of marketing channels? The main types of marketing channels are direct, indirect, and hybrid channels. Direct channels involve selling directly to the consumer, while indirect channels involve intermediaries like retailers or wholesalers. Hybrid channels use a mix of both.
- How do marketing channels affect customer experience? Marketing channels directly influence how customers interact with businesses, affecting their shopping experience. A seamless, efficient channel can lead to better customer satisfaction, while poor channel management can lead to frustration and lost sales.
- What is the role of intermediaries in marketing channels? Intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, and agents, facilitate the movement of products from producers to consumers. They play a vital role in managing inventory, distribution, and customer relationships.
- Why is channel management important for businesses? Channel management ensures that products reach consumers efficiently and that all parties involved in the channel are aligned and working toward the same goals. It helps businesses optimize their distribution strategies and improve overall sales performance.
- How do digital marketing channels differ from traditional ones? Digital marketing channels, such as social media, email marketing, and e-commerce platforms, provide businesses with real-time access to customers and allow for more personalized, data-driven strategies. Traditional channels, like physical retail stores and print advertising, are more static and less flexible.